6 best foods to include in your post-workout meal
Personally, I love doing strength training. I know nutrition plays a big role in muscle recovery, so I documented myself on which foods and supplements are best to include in my post-workout meals.
Just in case you were wondering, I did not include these fancy bodybuilder supplements that are running on the internet. I don't think they are necessary and research shows the same. My recommendations are affordable and easy to get, all coming from whole-foods; except one that I decided to include due to its gut and immune health benefits.
You can find most of them in nutrition central! Here you can see the brands I take and order them for yourself.
How Your Body Is Affected By Physical Activity
When you work out, your muscles use the glycogen stores, which partially depletes these glycogen stores. Exercise also breaks down proteins of your muscles. After the workout, your body tries to rebuild its glycogen stores and repair and regrow those muscle fibres.
It is particularly important to eat proteins and carbohydrates after the work out in order to help your body heal. Thus, this will decrease muscle protein breakdown, increase protein synthesis, restore glycogen stores and enhance recovery.
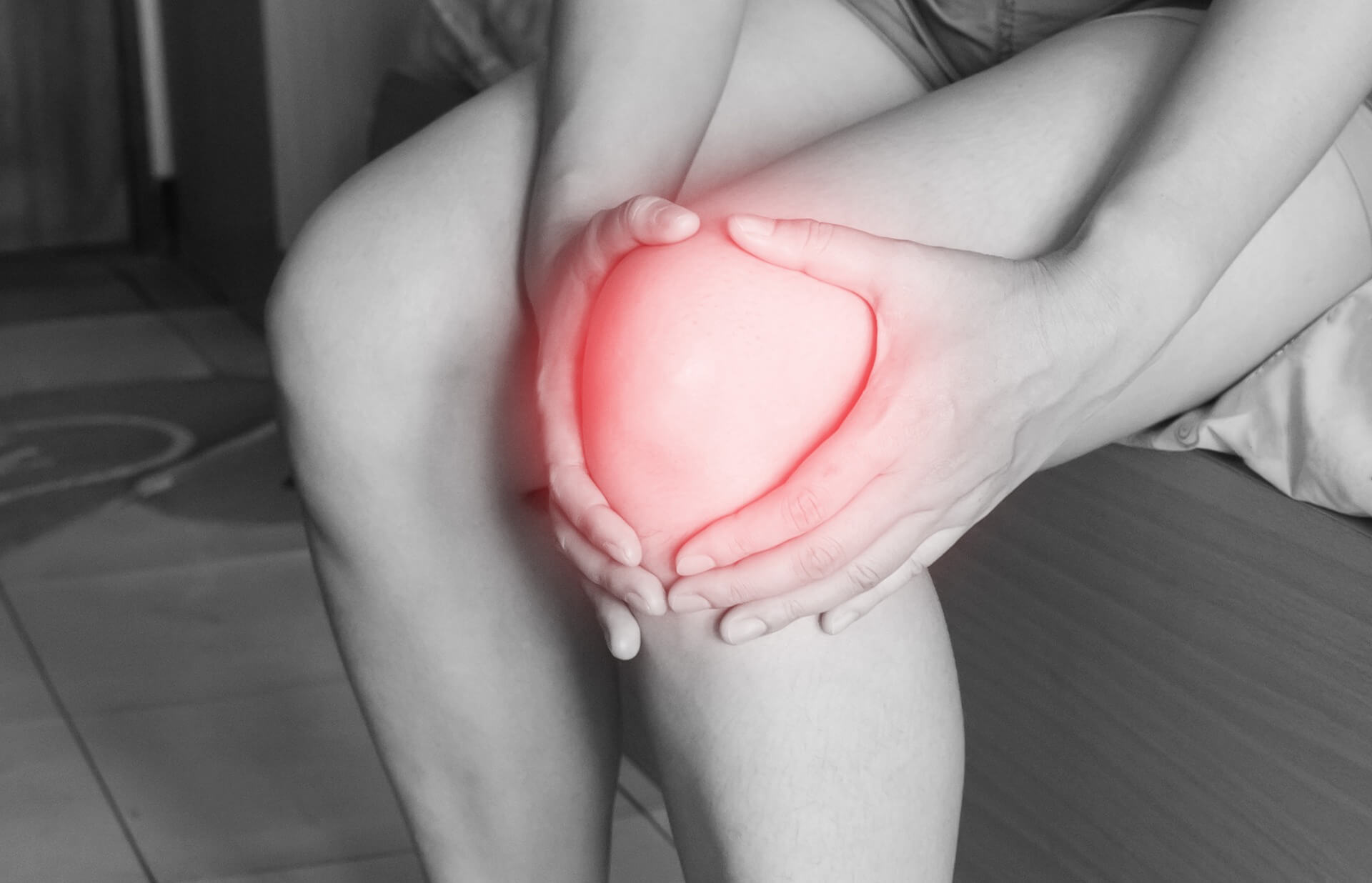
Exercise Increases Inflammation
Heavy physical exercise induces muscular injury leading to inflammation and oxidative stress (imbalance between oxidant and antioxidant levels), which can create changes in gene expression.1, 2 Antioxidant foods are recommended to counteract the negative effects of oxidative damage due to free radicals. Anti-inflammatory foods will also have a positive effect on body recovery.
Most studies have assessed the positive effects of antioxidant-rich foods on exercise performance for at least 7 days, and up to 60 days.3 It is important that you keep a high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory diet as part of a healthy lifestyle, not just for a brief period of time. And, by the way, antioxidants have to come from whole-foods, not via antioxidant supplementation. Supra-physiological doses of antioxidants have not been linked to health benefits, but to the contrary.2
Exercise Produces Changes In The Immune System
Studies have shown that exercise produces changes in the immune system.3 For a long time, it was thought that the immune system is suppressed after exercise because immune cell counts in the blood tended to be lower. However, recent research has clarified that this reduction is due to most immune cells relocate to places such as lungs, where they look for infections. Contrary to what it was though, the immune system is boosted after exercise!4
Carbohydrates and high-protein post-workout meals have been shown to restore immune function (attenuate exercise-induced increases in circulating cytokines and immune cells). Fruits, vegetables and grains, which are high in antioxidant compounds, are also thought to improve immune system parameters.5
Protein Helps Repair And Grow Muscle
Since your muscles are damaged, it is important to provide your body with the amino acids needed to rebuild these proteins.
Studies have shown that to maximize muscle recovery, it is recommended to ingest 20-25 gr of protein after exercise.2

Carbohydrates Are Also Important
Because glycogen stores are used during exercise, consuming carbohydrates after exercise helps replenish them.5 Some types of exercise use glycogen stores faster than others. For example, endurance sports (cardio) require higher glycogen than resistance training (lifting weights).
Somewhere between 1.1-1.5 gr/kg of body weight is thought to be ideal.6
Moreover, amino acid uptake is shown to be greater when proteins are combined with carbohydrates post-workout.7 Insulin secretion, which promotes glycogen synthesis, is better stimulated when carbs and protein are consumed at the same time.7, 8
Is Timing Important For Post-Workout Meals?
While it is recommended to ingest proteins and carbohydrates within 45 minutes after exercise, it is not always necessary if you have taken a big pre-workout meal. In this case, your body might still be benefiting from it.5, 9, 10
Best Foods And Supplements For Exercise Recovery
Any food containing carbohydrates and proteins will be ideal as a post-workout meal, but I want to mention some specific foods and supplements I like to consume as well. Because most of these foods are anti-inflammatory, contain antioxidants and proteins, they are a great addition to help your body recover quicker. And, of course, all the information is science-baked!
 L-glutamine: glutamine is one of the most abundant amino acids in muscle and plasma, and one of the preferred sources of fuel for intestinal and immune cells.11 Glutamine is considered important, not only for promoting muscle growth12 and affecting immune cell proliferation, but also for being intermediates in the synthesis of DNA and RNA synthesis.13 Recently I made a post talking about other health benefits of L-glutamine.
L-glutamine: glutamine is one of the most abundant amino acids in muscle and plasma, and one of the preferred sources of fuel for intestinal and immune cells.11 Glutamine is considered important, not only for promoting muscle growth12 and affecting immune cell proliferation, but also for being intermediates in the synthesis of DNA and RNA synthesis.13 Recently I made a post talking about other health benefits of L-glutamine.
 Protein powder: because protein requirements are higher when doing strength training,12 protein supplements can be a great addition to your diet. They are not necessary at all, but they can be very handy. I always choose for plant-based protein supplements. Why? I am planning to write a post about it soon! For now, this is the protein powder I use.
Protein powder: because protein requirements are higher when doing strength training,12 protein supplements can be a great addition to your diet. They are not necessary at all, but they can be very handy. I always choose for plant-based protein supplements. Why? I am planning to write a post about it soon! For now, this is the protein powder I use.
 Cacao powder: contains cocoa flavanols, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It has been suggested that these flavanols may improve exercise performance and recovery. Even though literature is a mixed,14, 15 one systematic review found enough evidence for the effectiveness of these compounds in reducing oxidative stress caused by exercise and improving vascular function.16 I, personally, enjoy adding cacao powder to my protein muffins, oatmeal and yoghurt. It’s a healthy way to add flavour and antioxidants to your sweet meals!
Cacao powder: contains cocoa flavanols, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It has been suggested that these flavanols may improve exercise performance and recovery. Even though literature is a mixed,14, 15 one systematic review found enough evidence for the effectiveness of these compounds in reducing oxidative stress caused by exercise and improving vascular function.16 I, personally, enjoy adding cacao powder to my protein muffins, oatmeal and yoghurt. It’s a healthy way to add flavour and antioxidants to your sweet meals!
 Spirulina: nowadays is a popular nutritional supplement, which I totally support. It’s something I have been taking for years now. Apart from having antioxidants, spirulina is made of 57% protein! Research suggests that this blue-green alga could improve exercise performance and fat oxidation,17 prevent skeletal muscle damage18 and may protect against a deficit in immune function.19
Spirulina: nowadays is a popular nutritional supplement, which I totally support. It’s something I have been taking for years now. Apart from having antioxidants, spirulina is made of 57% protein! Research suggests that this blue-green alga could improve exercise performance and fat oxidation,17 prevent skeletal muscle damage18 and may protect against a deficit in immune function.19
 Berries and pomegranate: rich in several substances (phenolic compounds, flavonoids, carotenoids and ascorbic acid) with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Blueberries used in the context of exercise-induced muscle damage showed positive results regarding oxidative stress and force recovery, but not for the muscle soreness.20 On the same line, studies have also pointed out the positive results of ingestion of pomegranate juice in regards to reduction of soreness and attenuation of weakness. Pomegranate also inhibits oxidative processes within the body.21
Berries and pomegranate: rich in several substances (phenolic compounds, flavonoids, carotenoids and ascorbic acid) with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Blueberries used in the context of exercise-induced muscle damage showed positive results regarding oxidative stress and force recovery, but not for the muscle soreness.20 On the same line, studies have also pointed out the positive results of ingestion of pomegranate juice in regards to reduction of soreness and attenuation of weakness. Pomegranate also inhibits oxidative processes within the body.21

 Oats: contain β-glucans, a type of polysaccharides found as well in mushrooms, barley and yeast. Receptors for these polysaccharides are found in a wide variety of immune cells and fibroblasts (connective tissue). While animals studies have shown improvements in exercise-induced stress,22 there is still some mixed evidence in humans for this substance.23, 24, 25 In any case, oats are a great source of carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Oat porridge is a tasty and great post-workout meal that will give you the energy you need to recover.
Oats: contain β-glucans, a type of polysaccharides found as well in mushrooms, barley and yeast. Receptors for these polysaccharides are found in a wide variety of immune cells and fibroblasts (connective tissue). While animals studies have shown improvements in exercise-induced stress,22 there is still some mixed evidence in humans for this substance.23, 24, 25 In any case, oats are a great source of carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Oat porridge is a tasty and great post-workout meal that will give you the energy you need to recover.
Now, go prepare that chocolate oatmeal bowl! If you want a savoury post-workout instead, any meal containing carbohydrates and proteins will be perfect too. How about a veggie tofu stir-fry?




